Examining B12 Shots & Injections: Highlighting Their Usage, Including the Trend of B12 Shots at Parties.
Exploring B12 Shots & Injections: Understanding the Risks, Including Instances of B12 Injection botched or Errors.
Exploring B12 Shots & Injections: Considering the Effects of B12 Shot Hangover Symptoms.
Delving into B12 Shots & Injections: Understanding the Administration Tool, Including the Use of a B12 Syringe for Delivery.
Discussing B12 Shots & Injections: Highlighting Concerns Surrounding Cyanocobalamin unhealthy Potential Negative Health Effects.
Examining B12 Shots & Injections: Addressing Potential Risks and Health Hazards Associated with Dangers of B12 Injections.
Med Spa: Facilities that offer medical treatments alongside spa services for holistic wellness and rejuvenation.
Discussing B12 Shots & Injections: Examining Their Role in the Context of the Body Positivity Movement, Which Advocates for Acceptance and Celebration of All Body Types.
Examining B12 Shots & Injections: Addressing Changes in Appetite, Commonly Termed as ‘Body Started Eating’
Examining Discomfort Levels: Addressing the Perception of Pain Associated with B12 Shots & Injections, Often Described as ‘So Much Pain’.
Explore B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative, featuring insights from the esteemed Baby Ken.
Navigate through B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative, including insights on managing cleft lip.
Exploring the world of Vitamin B12 shots: Unveiling the Good, the Bad, and Alternative paths to wellness with the definitive benefits and considerations of vitamin B12 shots.
Explore the landscape of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Uncovering the pros, cons, and alternatives, with a detailed look at the benefits of the vitamin B12 injection.
Unlocking the secrets of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: A comprehensive guide to the positives, negatives, and alternative choices in the world of vitamin shots.
Explore B12 Shots & Injections: Uncover ‘What is a B12 injection,’ weighing the pros, cons, and alternatives for well-informed choices.
Exploring B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Analyzing the Definite Benefits and Risks of Lipo B12 Shots, Alongside Alternative Methods.
Understanding B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Addressing the Definite Concerns When a B12 Injection Gone Wrong, and Exploring Alternative Approaches.
Discussing B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Addressing the Definite Connection to Folate Deficiency Anaemia and Exploring Alternative Treatment Approaches.
Exploring B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Understanding the Definite Impact on Red Blood Cells and Exploring Alternative Methods for Nutrient Delivery.
Examining B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Investigating the Definite Relationship Between B12 Injections and Weight Loss, Alongside Alternative Approaches.
Analyzing B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Considering the Definite Role of Dietary Supplements in Comparison to Traditional Injection Methods.
Exploring B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Assessing the Definite Risks of Allergic Reactions and Investigating Alternative Delivery Methods.
Discussing B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Examining the Definite Relationship Between B12 Injections and Folic Acid Levels, Alongside Alternative Supplementation Options.
Explore the spectrum of B12 Shots & Injections: From risks to rewards, find a safer alternative with PatchMD Vitamin Patches, steering clear of the pitfalls of B12 injections gone wrong.
Decipher the landscape of B12 Shots & Injections, exploring the nuances and essential B12 injection indications for a well-informed approach to supplementation.
Navigate the landscape of B12 Shots & Injections, discerning the pros and cons, and embrace the convenience of PatchMD Vitamin Patches, leaving behind the hassle of B12 needles.
Explore B12 Shots & Injections: Pros, cons revealed; PatchMD offers a needle-free alternative, bypassing B12 shorts hassle.
Uncover the intricacies of B12 Shots & Injections, assessing the merits and pitfalls, and find B12 shots for sale with PatchMD’s innovative and convenient alternative.
Explore the landscape of B12 Shots & Injections, weighing the pros and cons, and consider the innovative biitamin B12 injection alternative from PatchMD for optimal supplementation.
Delve into the world of B12 Shots & Injections, exploring the pros and cons, and discover if ‘Can I give myself B12 injections?’ with insights and alternatives from PatchMD.
Navigate B12 Shots & Injections: Weigh the pros, cons, and discover a convenient alternative, minimizing medical and lab appointments with PatchMD Vitamin Patches.
Local Waste Disposal Company: Explore B12 Shots & Injections, assessing the pros and cons, and opt for PatchMD’s convenient alternative, sparing local waste disposal companies from needle-related concerns.
Explore B12 Shots & Injections: Understand the pros, cons, and consider alternatives to mitigate serious symptoms with PatchMD.
Dive into B12 Shots & Injections: Uncover pros, cons, and explore alternatives if adverse effects occur with PatchMD.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative! Exploring the benefits and drawbacks of B12 injections, while delving into the intriguing realm of the B12 vaccine as a definite alternative.
Half Life of B12 Injection:Explore the realm of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Uncover the vital details, including the definitive half-life of B12 injection, to make informed choices for your health journey.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative! Unveiling the truth about the benefits and drawbacks, one definite concern echoed by many – the arm hurts after B12 shot.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Unraveling the Mystery Behind the Buzz! Explore the Good, Bad, and Alternative Aspects of B12 Injection Why.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Navigating the Terrain of Vitality! Unveiling the good, confronting the bad, and exploring alternatives, all while addressing the definite link to folate deficiency.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Navigating the Pros and Cons, with a Definite Focus on Folate Deficiency Anaemia Alternatives!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Unveiling the crucial role in treating folate deficiency anaemia, these injections offer a definitive solution to replenish essential nutrients and promote overall well-being.
Treat Folate Deficiency AnaemiaB12 Shots & B12 Injections: Navigating the Landscape of Vitamin B12 Benefits and Drawbacks, including the Definite Role in Treating Folate Deficiency Anaemia!
Dive into the comprehensive guide on B 12 shots, exploring their benefits, risks, and alternatives to make informed decisions about your health and wellness journey with B12 shots.
Uncover the complete spectrum of B12 liquid shots, delving into their advantages, drawbacks, and alternative solutions in our in-depth exploration of B12 Shots & Injections
Discover the comprehensive breakdown of the benefits and drawbacks of the monthly B12 injection, exploring its role in B12 Shots & Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!
Explore the full spectrum of benefits and considerations surrounding vitamin B-12 injections in our detailed analysis of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!
Delve into a comprehensive analysis of B 12 injection side effects as part of our extensive exploration in B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!
Discover how B12 Shots & B12 Injections relate to maintaining optimal health within the context of a vegetarian or vegan diet in our comprehensive exploration.
Explore the spectrum of B12 solutions beyond the needle with our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” Discover the effectiveness and convenience of vit B12 injection alternatives, offering the same benefits in non-invasive forms like patches or oral supplements for your health journey.
Another Name for Vitamin B12 Injection: Delve into our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” and explore the various names associated with vitamin B12 injections, such as cyanocobalamin injection or hydroxocobalamin injection, uncovering the diverse options available for B12 supplementation.
Are B12 Shots Worth It: In our guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” we delve into whether B12 shots are worth it, weighing the pros and cons to help you make an informed decision about this supplementation method and exploring viable alternatives for your health and wellness needs.
Within our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” we explore the concept of a B12 cocktail shot—a blend of vitamins and nutrients including B12—evaluating its benefits and considerations, offering insights into this popular injection method for potential health improvements.
Dive into our detailed guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” as we unravel the world of B12 injectables, providing comprehensive insights into the different forms, benefits, and considerations surrounding these injectable B12 supplements for your informed health choices.
Explore our in-depth guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” to uncover a comprehensive B12 injection review, where we dissect the effectiveness, potential side effects, and user experiences, providing a detailed analysis to help you make informed decisions about B12 supplementation via injections.
Within our guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” we explore the role of folic acid in conjunction with B12 supplementation, highlighting its importance in supporting red blood cell production, DNA synthesis, and overall cellular health, emphasizing the synergy between these two essential nutrients.
In our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” we address the possibility of experiencing an unusual or allergic reaction to B12 injections, detailing the signs, symptoms, and steps to take if such a reaction occurs, ensuring safety and informed decision-making regarding B12 supplementation methods.
In our thorough exploration within “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” we delve into the interactions of B12 injections with other drugs, shedding light on potential conflicts, synergies, or effects these injections might have when taken alongside different medications, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for safe supplementation.
Within our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” we discuss the role of dairy foods in providing natural sources of B12, highlighting how dairy, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, can contribute to fulfilling your B12 dietary requirements, offering an alternative to supplementation for some individuals.
In our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” we explore the implications of B12 supplementation for individuals with kidney disease, discussing how impaired kidney function can affect B12 levels and the considerations required when supplementing, ensuring safe and appropriate choices for those managing kidney conditions.
Delve into our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!” where we dissect the complexities of drug interactions concerning B12 injections, outlining potential conflicts or synergies between B12 supplements and various medications, empowering informed decisions for safe and effective supplementation.
Lipo B12 shot, a fusion of Vitamin B12 and lipotropic compounds, offer PatchMD’s innovative approach to injectable supplementation, providing enhanced fat metabolism and energy boost, alongside essential B12 benefits in a convenient patch format.
Define B12 Injections: B12 injections, a method of delivering Vitamin B12 directly into the bloodstream, are a common approach to swiftly replenish B12 levels, offering a rapid and effective way to address deficiencies or boost energy and overall health.
Vitamin B12 methylcobalamin injection, a specialized form of B12 supplementation, provide a highly bioavailable and active form of B12, supporting nerve health, energy production, and overall well-being through direct administration into the body.
Adenosylcobalamin injection, a specific type of Vitamin B12 supplementation, offer a bioactive form of B12 crucial for energy metabolism, nerve function, and cellular health when administered directly into the body, supporting overall vitality.
Are B12 Shots Methylated: B12 shots can contain methylated forms of B12, such as methylcobalamin or adenosylcobalamin, which are readily usable by the body and can offer enhanced bioavailability compared to non-methylated forms, aiding in various bodily functions and overall health.
Active forms refer to bioavailable versions of Vitamin B12, like methylcobalamin or adenosylcobalamin, which are readily usable by the body upon administration in B12 shots or injections, supporting essential functions like energy production, nerve health, and red blood cell formation.
The active form of B12 in shots or injections typically refers to methylcobalamin or adenosylcobalamin, which are bioavailable and readily utilized by the body for essential functions like energy production, nervous system health, and red blood cell formation.
The term human body refers to the entire physical structure and system of organs, tissues, and cells that constitute a person, where B12 shots or injections can directly deliver Vitamin B12 to support crucial bodily functions such as energy production, nervous system health, and red blood cell formation within this complex biological system.
The synthetic form of B12 in shots or injections denotes laboratory-created versions of Vitamin B12, which can mirror the structure and function of naturally occurring B12. While effective in supplementing B12 levels, they are not derived from natural food sources and are formulated to mimic the active forms of B12 found in the body.
Amino acid metabolism is the biochemical process in the body responsible for breaking down proteins into their constituent amino acids and utilizing them for various bodily functions. B12 shots or injections can support this process by aiding enzymes that facilitate amino acid metabolism, contributing to energy production and overall cellular health.
Boosting Health with B12 Shots: Pros, Cons, and Alternatives
If you’ve ever considered vitamin B12 shots to boost your energy levels or address a deficiency, you may have wondered about their benefits and potential risks. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of B12 injections, examining their role in maintaining overall health, and exploring alternative supplementation methods with vitamin b12. By the end of this post, you’ll have the knowledge to make informed decisions about whether B12 shots are right for you.
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin B12 injections offer an effective solution for individuals with absorption issues to maintain healthy levels and avoid deficiency.
- It is important to recognize the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency and consult a healthcare professional in order to assess individual needs, potential risks, and benefits.
- Alternative supplementation methods such as patches or oral supplements are available for obtaining adequate vitamin B12 levels.
Understanding B12 Shots and Their Role in Health

Vitamin B12, predominantly found in animal and fortified foods, significantly contributes to red blood cell production, including the formation of red blood cells, and neurological function maintenance. While most people can obtain sufficient B12 through their diet, some may face health problems like vitamin B12 deficiency due to inadequate absorption.
Injections, often involving intramuscular administration, are prescribed for individuals with absorption issues or a diet lacking in vitamin B12 rich foods. One common method is the intramuscular injection.
The Importance of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, a crucial component of the vitamin B complex, is necessary for red blood cell formation and the development and maintenance of the nervous system. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, fatigue, and even cognitive decline. Research has suggested that vitamin B12 injections can help improve vitamin B12 levels in individuals with absorption issues, thereby enhancing their overall well-being.
Vitamin B12 injections are a vital treatment for those with pernicious anaemia, a condition characterized by a lack of intrinsic factor – a protein that binds and absorbs vitamin B12. Intrinsic factor binds with vitamin B12 in the small intestine, forming a complex that is essential for the vitamin’s absorption. This binding is necessary for the absorption of Vitamin B12, and when there is a lack of it, the body cannot absorb the vitamin efficiently, leading to deficiency. Various medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn’s disease, can also impact vitamin B12 absorption, making injections a valuable solution for affected individuals.
Gastric surgery, such as weight loss procedures, can also lead to vitamin B12 deficiency by reducing the number of cells needed to secrete stomach acid and intrinsic factor. In these cases, vitamin B12 injections offer a direct source of the vitamin, bypassing the digestive system and providing a faster, more efficient absorption.
Vegetarians and vegans may also encounter challenges in obtaining adequate vitamin B12 from their diet, as the vitamin is predominantly found in animal products. Vitamin B12 injections can be a useful supplementation method for vegans and vegetarians who might struggle to maintain healthy vitamin B12 levels through diet alone.
The Word of Vitamin B
Vitamin B is a collective term for a group of essential nutrients, each playing a unique role in maintaining health. Within the Vitamin B complex, there are several members, including Vitamin B1 (thiamine), Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (niacin), Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid), Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), Vitamin B7 (biotin), Vitamin B9 (folate), and notably, vitamin B12 (cobalamin). Each Vitamin B has distinct functions: Vitamin B1 is crucial for energy metabolism, Vitamin B3 assists in DNA repair, and Vitamin B9 is vital for cell growth. Vitamin B12, a unique member of the Vitamin B complex, stands out due to its complex structure and the necessity of intrinsic factor for its absorption. This particular Vitamin B is essential for nerve health, the formation of red blood cells, and DNA synthesis. Vitamin B12, unlike other Vitamin B members, is stored in the liver in significant amounts and is primarily found in animal-based foods. This makes vitamin B12 deficiencies a particular concern for those following vegetarian or vegan diets. The storage and absorption characteristics of vitamin B12 differentiate it from other Vitamin B vitamins, which are water-soluble and require regular replenishment in the diet.
Intrinsic Factor and Absorption Challenges
As previously noted, intrinsic factor is a key player in B12 absorption, as it binds to the vitamin, allowing for proper absorption. Individuals with diminished levels or gastrointestinal problems may have difficulty maintaining sufficient B12 levels and could find injections beneficial.
Certain medical conditions and surgeries can hinder the body’s ability to produce it, leading to an increased risk of vitamin B12 deficiency. In these cases, B12 injections provide a direct source of the vitamin, circumventing the digestive system and aiding in absorption.
Moreover, vegetarians and vegans who may not consume enough B12-rich foods are at a higher risk of developing a deficiency. B12 injections can offer a practical solution to maintain healthy levels of the vitamin while adhering to a plant-based diet.
The Benefits of B12 Injections Over Oral Supplements
Although oral vitamin B12 supplements are readily available, B12 injections offer several unique benefits. Injections provide a higher absorption rate compared to oral supplements, particularly for individuals with medical conditions that affect absorption. This can lead to more rapid and efficient management of deficiency symptoms unlike when you take an oral vitamin.
Enhanced Absorption for Certain Medical Conditions
B12 injections are especially beneficial for individuals with medical conditions such as pernicious anemia, celiac disease, and Crohn’s disease. These conditions can affect the absorption of vitamins and nutrients, including B12. B12 injections can help restore B12 levels and alleviate symptoms in those with these conditions.
Injections are also advantageous for individuals who have undergone gastric surgery, as the procedure can:
- Decrease the number of cells needed to secrete stomach acid and intrinsic factor in the gastrointestinal tract
- Help bypass absorption challenges
- Provide adequate levels of the essential vitamin
Immediate Increase in Blood Levels
B12 injections can raise blood levels of the vitamin within 48 to 72 hours. The absorption rate is typically higher than that of oral supplements, resulting in faster and more efficient management of deficiency symptoms.
This rapid increase in blood levels is particularly helpful for individuals with severe deficiency symptoms or those who require immediate intervention for medical conditions related to vitamin B12 deficiency.
Identifying the Need for B12 Shots

Understanding the appropriate timing for considering B12 shots is crucial for addressing deficiency and supporting overall health. Recognizing deficiency symptoms and understanding who is at increased risk can help guide the decision-making process.
Recognizing Deficiency Symptoms
Common indicators of vitamin B12 deficiency are:
- Numbness or a tingling sensation in the hands and feet
- Vision problems
- Memory retention issues
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Pallid skin
- Smooth tongue
Should you observe any of these symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional to assess the need for B12 shots is necessary.
It is also crucial to identify the underlying causes of deficiency. Some common causes of vitamin B12 deficiency include:
- Autoimmune pernicious anemia
- Dietary limitations, such as vegetarian or vegan diets
- Medical conditions that affect absorption, such as celiac and Crohn’s disease
Identifying the specific cause of deficiency can help guide treatment and prevention strategies.
Celiac Disease: Who Is at Increased Risk?
Certain populations are at a higher risk for vitamin B12 deficiency. Older adults may experience decreased absorption of B12 due to changes in the acids and enzymes required for its absorption. Additionally, individuals with autoimmune or gastrointestinal disorders, such as pernicious anemia, celiac, or Crohn’s disease, are more likely to be at risk of deficiency.
Vegetarians and vegans may also face challenges in obtaining adequate B12 from their diet, as the vitamin is predominantly found in animal products. In these cases, B12 injections can be a practical solution to maintain healthy levels of the vitamin while adhering to a plant-based diet.
Safety Profile and Possible Side Effects of B12 Shots

B12 injections are generally regarded as very safe. However, like any medical treatment, they may have potential side effects or risks. Being aware of these potential side effects can help individuals make informed decisions about whether B12 shots are the right choice for them.
Allergic Reactions and How to Handle Them
Allergic reactions to B12 injections are rare but can occur. Symptoms may include hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. In the event of a severe allergic reaction, known as anaphylaxis, it is advised to seek medical attention immediately.
If you experience an allergic reaction to a B12 shot, consult your healthcare professional to discuss alternative treatment options. They may recommend adjusting the dosage, using a different form of B12, or exploring other supplementation methods, such as oral supplements or patches.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
While B12 injections can provide numerous benefits, it’s important to consider potential risks and side effects before opting for this treatment. Some individuals may experience swelling at the injection site, mild diarrhea, or itching. More severe side effects are rare but can include low potassium, headache, dizziness, and chest pain.
When considering B12 injections, consult with a healthcare professional to discuss your individual needs, medical history, and potential risks associated with the treatment. They can help determine the best course of action for addressing your B12 levels and overall health.
B12 Shots for Non-Deficient Individuals (i.e. weight loss)
Even without a deficiency, some individuals might contemplate B12 injections as a strategy to boost energy, facilitate weight loss, or enhance mood. While there may be anecdotal evidence supporting these claims, it’s essential to examine the scientific research to understand the potential benefits and risks of using B12 injections for purposes beyond deficiency treatment.
Investigating Claims Beyond Deficiency Treatment
There is evidence to suggest that B12 injections can enhance energy levels in individuals with an existing vitamin B12 deficiency. However, vitamin B12 injections have not been proven to increase energy or promote weight loss in individuals who do not have a deficiency. Studies have also not indicated any efficacy of B12 injections in improving cognitive function or mental health.
Some anecdotal evidence points to a potential connection between vitamin B12 shots and improved skin health or anti-aging effects. However, further research is required to confirm a direct link between vitamin B12 shots and these benefits.
When B12 Shots May Not Be Necessary
If you don’t have a B12 deficiency, injections might not be needed or advantageous. A balanced diet should provide most individuals with adequate vitamin B12 levels, and supplementation in the form of oral supplements or patches may be sufficient for those with specific dietary limitations or absorption issues.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before considering vitamin B12 injections, as they can help determine the appropriate dosage and administration method based on individual needs and medical history. They can also recommend alternative supplementation methods, such as oral supplements or patches, if injections are not necessary or appropriate for your situation.
Dietary Sources and Alternatives to Injections
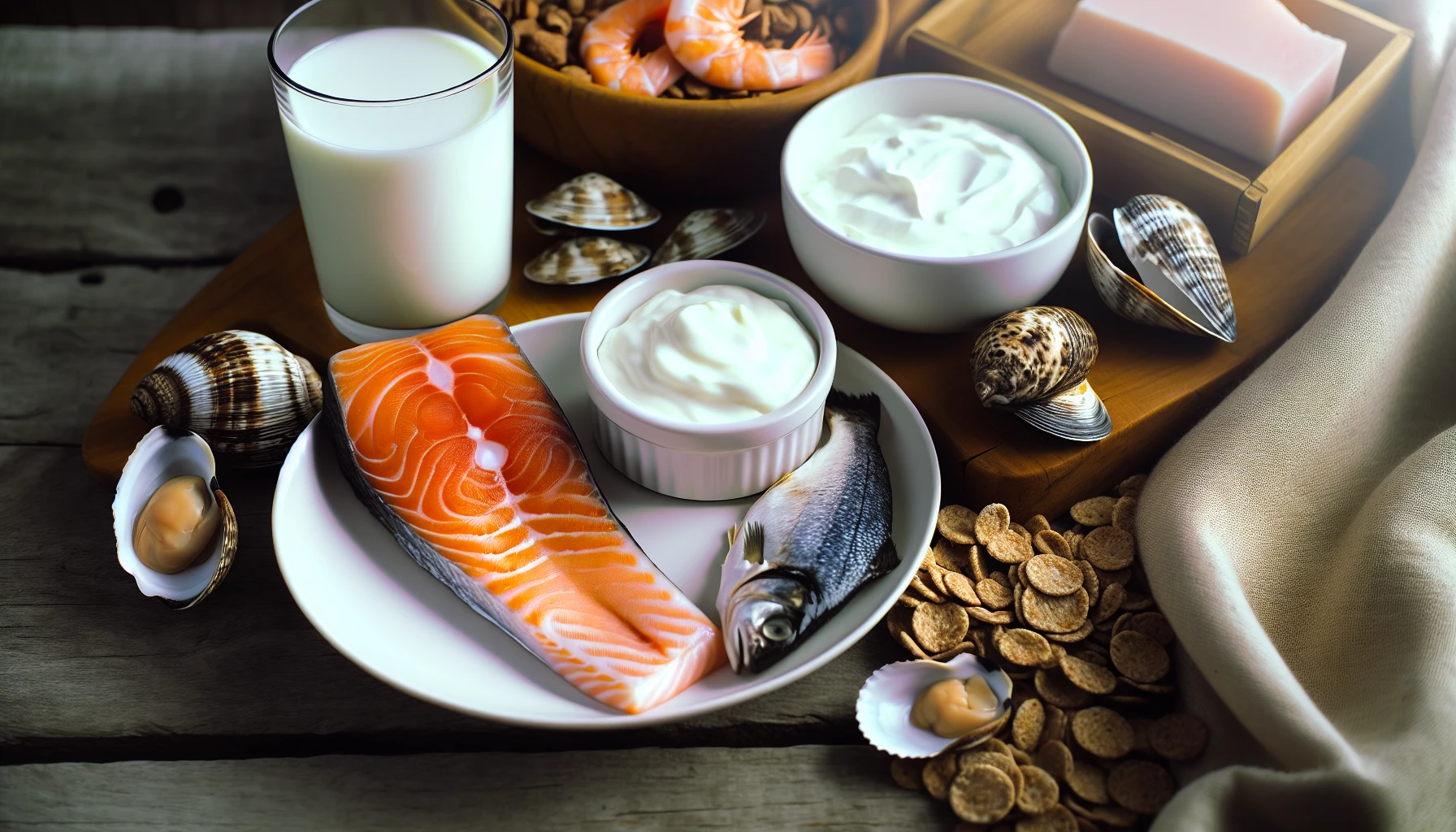

In addition to injections, there are other ways to ensure your body receives adequate Vitamin B12. Consuming a diet rich in B12-containing foods and exploring alternative supplementation methods, such as patches or oral supplements, can help maintain healthy vitamin B12 levels and support overall health.
Rich Dietary Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is usually found in fortified foods and animal foods, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Animal foods particularly high in vitamin B12 include bluefin tuna, Pacific oysters, salmon, Atlantic herring, mackerel, sardines, trout, and tuna. Beef and pork are also abundant sources of B12, as are poultry and fish. One hard-boiled egg contains approximately 0.6 micrograms of B12, or about 25% of the recommended daily value.
For those who don’t consume animal foods, such as vegetarians and vegans, there are plant-based sources of vitamin B12 available, including nutritional yeast, fortified foods, cereals, mushrooms, and certain types of algae.
Oral Vitamin B12: A Viable Option?
Considering the growing evidence supporting the effectiveness of oral vitamin B12 supplements, they may be a viable alternative to injections for many individuals. One study found that high doses of oral B12 (1,000 mcg daily) could provide adequate absorption even in the presence of intrinsic factor deficiency.
Oral vitamin B12 supplements have several advantages over injections:
- They are more cost-effective
- They are more convenient, as they do not require a visit to a healthcare facility or a home visit from a healthcare professional for administration
- The risk of an allergic reaction is typically lower with oral supplements than with injections.
If you’re not experiencing a vitamin B12 deficiency and are exploring supplementation options, oral B12 supplements may be a practical alternative to injections. Always consult with a healthcare professional before taking any new oral vitamin to ensure it is appropriate for your individual needs and health history.
Navigating B12 Injection Protocols
To effectively treat deficiency and manage it in the long term, determining the correct dosage and schedule for vitamin B12 injections is necessary. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to tailor the correct dosage and frequency based on your individual needs and medical history.
Determining the Right Dose and Schedule
The dosage of vitamin B12 injections may vary depending on factors such as sex, age, weight, diet, and other individual factors. A healthcare professional can help determine the appropriate dosage for your specific requirements. The recommended dosage for B12 injections in adults is generally 100 mcg (0.1 mL) daily for 6 or 7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 1,000 mcg once a month.
The frequency of vitamin B12 injections may also vary depending on your individual needs and response to treatment. Daily injections may be administered for a certain period of time, followed by a reduced frequency depending on your response and requirements. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable frequency of B12 injections for your health condition.
Long-Term Management of B12 Deficiency
Managing vitamin B12 deficiency in the long-term typically involves:
- Regular B12 supplementation, either through injections or oral therapy
- Dosage can vary from 1 to 5 mg daily
- Administered over a period of one to four months or until laboratory results indicate improvement in hematologic and/or neurologic functions
Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on managing vitamin B12 deficiency in the long-term and determining the most appropriate supplementation method for you.
If vitamin B12 injections are not suitable or necessary for your situation, alternative supplementation methods such as oral supplements or patches may be recommended by your healthcare professional. By closely monitoring your symptoms and vitamin B12 levels, you can ensure adequate levels of this essential vitamin and maintain overall health.
B12 Shot Alternatives
Beyond injections, there are other vitamin B12 supplementation options like patches and oral supplements. These alternatives may offer a more convenient and cost-effective approach to addressing vitamin B12 deficiency or maintaining healthy vitamin B12 levels for individuals who do not require injections.
B12 Vitamin Patches by PatchMD
B12 Vitamin Patches by PatchMD are transdermal patches that provide direct delivery of vitamin B12 into the bloodstream through the skin. These patches offer a convenient and effective way to supplement vitamin B12 levels in the body, especially for individuals who may have difficulty absorbing oral supplements due to medical conditions or other factors. The patches should be applied to clean, dry skin and can be worn for up to 8 hours.
B12 patches by PatchMD have been known to:
- Increase energy levels
- Sharpen focus and attention
- Reduce stress and anxiety
- Treat vitamin deficiency
As a preferable alternative to B12 shots and oral supplements, these patches can be an excellent option for those seeking a convenient and effective method of Vitamin B12 supplementation.
Shop the B12 Energy Patch today and discover this natural source of energy for yourself. After all, what do you have to lose except pain and discomfort? Your freedom is one step away.
B12 Oral Supplements
As an alternative to injections, oral vitamin B12 supplements offer a convenient and economical method of supplementation. Several studies have indicated that the efficacy of oral vitamin B12 supplements is comparable to that of vitamin B12 injections. One study found that high doses of oral B12 (1,000 mcg daily) could provide adequate absorption even in the presence of intrinsic factor deficiency.
Oral supplements are generally more convenient than injections, as they do not require a visit to a healthcare facility or a home visit from a healthcare professional for administration. Furthermore, the risk of an allergic reaction is typically lower with oral supplements than with injections.
Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new dietary supplements regimen to ensure it is appropriate for your individual needs and health history.
Summary
In conclusion, vitamin B12 injections can provide numerous benefits for individuals with a deficiency or those with medical conditions that affect absorption. However, it’s essential to weigh the potential risks and side effects and consider alternative supplementation methods, such as oral supplements or patches, when appropriate. By understanding the importance of vitamin B12, recognizing deficiency symptoms, and consulting with a healthcare professional, you can make informed decisions about your B12 supplementation needs and maintain overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a B12 injection do to you?
B12 injections can reverse or prevent a deficiency, help maintain red blood cells, and increase energy levels, brain function, mood, metabolism, and weight loss by boosting the production of red blood cells.
Do B12 injections really work?
Yes, B12 injections are very effective at reversing and preventing a vitamin B12 deficiency, as they allow for 100% absorption directly into the tissues. They can improve symptoms such as numbness and tingling, weakness, difficulty walking and memory trouble, as well as reduce anemia and fatigue.
How many days does a B12 shot last?
The effects of a B12 shot typically last from 48-72 hours, though some people can experience benefits for several weeks to months.
What are signs you need B12 shot?
Signs that you may need a B12 shot include fatigue, pale skin, weakness, shortness of breath and loss of appetite. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s best to speak with a doctor to determine the cause and discuss whether a B12 injection is necessary.
What are the primary causes of vitamin B12 deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency is primarily caused by autoimmune pernicious anemia, dietary restrictions such as vegetarian or vegan diets, and medical conditions that interfere with absorption such as celiac and Crohn’s disease.
Who might need Vitamin B supplements?
Individuals who may benefit from Vitamin B supplements include those with dietary restrictions (like vegans, who might lack vitamin B12), the elderly, those with certain medical conditions, pregnant women (who may need more Vitamin B9), and anyone with a diagnosed deficiency in one or more Vitamin B nutrients.
Are there any risks associated with taking Vitamin B supplements?
While Vitamin B supplements are generally safe, excessive intake of certain Vitamin B types, like Vitamin B6 and Vitamin B3, can lead to adverse effects. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Can I get enough Vitamin B from my diet?
A balanced diet can provide adequate amounts of Vitamin B for most people. However, certain lifestyles or health conditions might lead to a deficiency in one or more Vitamin B vitamins, necessitating supplements. Foods rich in Vitamin B include whole grains, meats, eggs, dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and legumes.
About PatchMD B12 Patches
The B12 Energy Topical Patch is the best natural method of boosting energy, focusing attention and reducing anxiety without the burden of pills or injections.
For many decades, physicians and health experts have touted the benefits of Vitamin B12 to boost energy while creating a natural sense of well-being. With the slow release technology of a topical patch, we provide you with 24-hour access to this positive source of health. The B12 Energy Patch is a safe, effective and inexpensive alternative to prescription injections and oral supplements. In addition, our effective delivery system avoids the negative absorption issues of these other methods. Utilizing a patch delivery system, you can also help avoid a deficiency in this super vitamin.
Other Resources:
- The Best Foods for Anti-aging, Optimal health, and Maintaining Youthful Skin
- Fat-Soluble vs. Water-Soluble: Comparing Vitamins’ Absorption Abilities
- B12 Vape – The Good, The Bad & The Alternative
- Best Supplements for Weight Loss and Muscle Gain
- Everything You Need to Know About Taking Topical Biotin
- How Are Vitamins Absorbed Through Your Skin? The Science Behind Patches
- Magnesium for Anxiety: What You Need to Know
vitamin shots and vitamin b shots
Most people who have low levels of vitamin b get vitamin b shots to increase their levels. Low levels of vitamin b can be dangerous and vitamin b12 shots can really help. If you dont want to get b12 shots then you can try eating foods rich in vitamin b such as dairy products. Many foods have natural sources of vitamin b. Dairy products can be a helpful addition to your diet if you’re looking to increase your vitamin b levels. Many foods like animal products such as salmon are high in vitamin b.
health
mayo clinic
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Exploring the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Unveiling the significance of the B12 daily dose for a comprehensive understanding of its benefits and potential drawbacks.
Navigating the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Delve into the unique realm of B12 liposomal delivery methods, shedding light on a distinctive approach for optimal absorption and effectiveness.
Weighing the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Explore the realm of B12 powder for water, a novel approach offering convenience and versatility in supplementing your daily vitamin B12 needs.
Decoding the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Uncover the nuances between B12 strips vs pills, providing insights into the contrasting benefits and considerations for choosing the most suitable supplementation method.
Evaluating the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Navigate the considerations and precautions when it comes to buying B12 injections, ensuring informed choices for optimal health and well-being.
Unveiling the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Explore the synergies with other B vitamins, uncovering the holistic benefits and potential interactions that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of your supplementation choices.
Navigating the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Tailoring insights to the unique needs of older adults, unravel the considerations and benefits associated with B12 supplementation in this demographic for enhanced well-being.
Exploring the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Delve into the recommendations from the Food and Nutrition Board to gain a comprehensive understanding of the guidelines shaping B12 supplementation practices for optimal health.
Homocysteine Lowering B Vitamins: B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Investigating the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Uncover the role of homocysteine-lowering B vitamins, particularly B12, in promoting cardiovascular health and delve into the potential benefits within the spectrum of supplementation options.
Assessing the Good, Bad, and Alternative! Explore how B12 supplementation intersects with health considerations, deciphering whether it acts as a risk factor or a beneficial element in the complex landscape of wellness.
In our comprehensive guide on ‘B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!’ uncover everything you need to know, including the definitive source to buy methylcobalamin B12 injections for your wellness journey.
Delve into ‘B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!’ to definitively uncover the link: can B12 injections cause acne, addressing concerns while exploring the full spectrum of effects for informed health decisions.
In our comprehensive guide, ‘B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad and Alternative!’, we definitively address the query: can B12 shots cause acne? Unravel the truth behind potential side effects for a well-rounded understanding.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Exploring the Good, Bad, and Alternatives, Unveiling the Definite Super MIC B12 Side Effect!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Navigating the Ups, Downs, and What to Do When Feeling Tired After B12 Shot!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Understanding the Benefits, Risks, and Managing Effects of Too Much B12 Injection!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Unveiling the Pros, Cons, and Strategies to Combat Muscle Cramps!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Assessing the Pros, Cons, and Effects that Linger for a Few Days!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Examining the Positives, Negatives, and Ways to Address Negative Reactions!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Navigating the Spectrum – From Benefits to Coping with Severe Symptoms!
Exploring the world of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Unveiling the Good, Bad, and Alternative Options, dissecting the realm of benefits and potential adverse reaction.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Exploring the Dynamics of this Water Soluble Vitamin – The Good, the Bad, and Alternative Approaches!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Discover the benefits and drawbacks of B12 shots, and explore the question on everyone’s mind: How quickly does B12 shot work? Uncover the facts to make informed decisions about your health.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Delve into the realm of methyl B12 injections benefits, unlocking insights into the unique advantages that this form of vitamin supplementation offers for your overall well-being.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Explore the benefits and drawbacks of B12 injections, and delve into shot B vitamins reviews to discover firsthand experiences and insights on their efficacy and potential side effects.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Uncover the nuances of well MB12, a highly bioavailable form of vitamin B12, as we explore its advantages and potential considerations in the realm of B12 supplementation.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Explore the advantages and considerations of 1st Step Pro Wellness B12 for a comprehensive understanding of this specific B12 supplement.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Delve into the debate: Are B12 shots better than pills? Uncover the pros and cons to make an informed decision about the most effective B12 supplementation method for you.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Explore the impact of B12 supplementation on mental and emotional stability, uncovering how these injections may play a role in promoting overall well-being.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Read insightful review write-ups to gain valuable perspectives on the efficacy and experiences of individuals who have incorporated B12 shots into their wellness routines.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Analyze the efficacy of various B12 supplements through a critical lens, as we delve into insightful perspectives encapsulated in each review’s title.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Navigate through the realm of B12 supplementation, addressing the concerns left unspoken in the empty question’s body.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Gain insights from the experiences of an anonymous user as we explore the diverse perspectives on B12 supplementation.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Don’t let your knowledge be an empty invalid email; uncover the facts about B12 supplementation to make informed decisions for your health.
Uncover the spectrum of B12 Shots & Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternatives! Plus, locate reliable ‘b12 shots near me’ for your convenience and health goals.
Dive into the world of B12 Shots & Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Also, explore transparent and definite ‘b12 injection prices’ to make informed choices for your health.
Exploring B12 Shots & Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Embrace the benefits with our definitive guide and find your ‘b12 love’ for optimal wellness.
Delve into B12 Shots & Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Discover reliable information and convenient options, including trusted ‘online pharmacy’ sources, for your B12 needs.
Navigate B12 Shots & Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Learn about the impacts on health, including insights into ‘weight gain’ factors, for a holistic understanding.
Explore the benefits and drawbacks of B12 shots and injections in our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Uncover the specifics of the sought-after B12 booster shot for a detailed perspective on this popular health trend.
Dive into the world of vitamin B12 with our guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Curious about the basics? Learn precisely “whats a B12 shot” as we unravel the mysteries behind this popular health phenomenon.
Discover a holistic perspective on B12 supplementation in our guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Delve into alternatives such as B12 drops, exploring their efficacy and potential benefits for those seeking diverse options for vitamin B12 intake.
Explore the world of B12 supplementation with our comprehensive guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Uncover unique insights, including the intriguing concept of “B12 Love San Jose,” shedding light on innovative approaches to B12 wellness in the San Jose community.
Navigate the realm of B12 supplementation in our guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Get a clear perspective on budget considerations with insights into the “B12 shot price,” helping you make informed decisions about the cost aspects of this popular health regimen.
Embark on a journey through B12 supplementation in our guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Explore regional perspectives, including the availability and benefits of “B12 shots Maryland,” offering insights into localized approaches to vitamin B12 wellness in the Maryland area.
Unlock the secrets to B12 supplementation with our guide, “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Delve into the connection between B12 and maintaining a “healthy weight,” discovering how this essential vitamin may play a role in your journey to overall well-being.
Explore the world of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Uncover the secrets of optimal health as we delve into what’s in a B12 shot, providing you with a definitive guide to make informed choices for your well-being journey.
Embark on a journey of informed wellness exploration with “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” as we dissect the pros and cons of B twelve injections, providing you with a definitive roadmap to navigate the diverse landscape of vitamin B12 supplementation.
Uncover the intersection of vitality and menopause in “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Delve into the crucial link between B12 and menopause as we provide a definitive exploration of how these injections can play a pivotal role in supporting women during this transformative phase of life.
Explore the optimal timing for B12 supplementation in “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” Discover the definitive benefits and considerations of taking B12 at night, unlocking the secrets to maximizing the impact of this essential vitamin on your overall well-being.
Navigate the landscape of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Gain a definitive understanding of potential risks as we delve into the topic of B12 injection allergy, ensuring you make informed choices on your path to optimal health.
In “B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative!” explore the critical considerations for emergency medical situations related to B12 injections. Gain a definitive understanding of the potential risks and necessary protocols, ensuring your health journey is well-informed and secure.
Exploring the realm of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Unveiling the importance of B12 injection sites in maximizing benefits and understanding potential drawbacks.
Dive into the realm ofB12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! , where science meets choice. Unravel the debate of biotin vs B12, as our meticulously crafted formulations provide clarity, allowing you to make informed decisions for your unique wellness journey.
Experience the convenience of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! your ultimate destination for health empowerment. Elevate your routine with precision-targeted nutrition, eliminating the need for traditional methods with our B12 injection CVS alternatives, redefining the way you nourish your body.
Embark on a journey withB12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! , where choices matter. Delve into the discourse of optimal B12 intake as we present a nuanced perspective on B12 injections versus oral supplements, empowering you to make informed decisions for a customized approach to your well-being.
Uncover the significance of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! , where health takes center stage. Navigate the realm of wellness with clarity as we decode the B12 shot meaning, offering a transformative understanding of targeted nutrition for a vibrant, balanced life.
Elevate your health journey with B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! , where precision meets choice. Unravel the intricacies of B12 supplementation as we guide you through the decision of B12 shot subq or im, empowering you to tailor your wellness approach with confidence and efficacy.
Discover the transformative potential of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! in combating nutritional gaps. Address the concern of biotin deficiency head-on, as our meticulously designed formulations offer a targeted solution to nourish your body and promote overall well-being.
Elevate your wellness routine with B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! , delivering unparalleled support. Immerse yourself in the world of optimal nutrition with our advanced biotin supplements, crafted to promote radiant skin, healthy hair, and overall vitality for a thriving, balanced lifestyle.
Unlock the potential of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! , where health meets innovation. Experience a tailored approach to well-being as our formulations nourish not just your body, but also your brain and nerve cells, fostering comprehensive support for a vibrant and resilient lifestyle.
Transform your self-care journey with B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! , designed to enhance your overall well-being. Experience the power of targeted nutrition as our formulations promote not only vitality but also support hair growth, revealing a holistic approach to beauty from the inside out.
Embark on a journey to optimal health with B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! , where precision meets wellness. Our meticulously crafted formulations go beyond the surface, supporting the health of your nerve cells and promoting a vibrant, resilient foundation for your overall well-being
Dive into the comprehensive guide on B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Uncover the role of vital nutrients, including the powerhouse of B12 found in beef liver, as we navigate through the nuances of supplementation.
“Exploring the realm of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Unveiling the query: ‘Does B12 injection have red dye?’ for a definite understanding of this crucial aspect in B12 supplementation.
Delving into B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Discovering the definitive answer to the question: ‘What is the best place for B12 injection?’ for optimal administration and effectiveness.
Navigating the landscape of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Unraveling the mysteries surrounding ‘CD B12. Shots’ for a definitive exploration into this unique form of B12 supplementation.
Embarking on a journey through B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Shedding light on the definite uses and benefits with ‘Vitamin B12 injection uses,’ providing a comprehensive understanding of its applications in health and wellness.
Exploring the diverse landscape of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Delving into the specifics with a focus on ‘B12 Aventura,’ unraveling unique aspects and potential alternatives in B12 supplementation.
Diving into the nuances of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Offering a definitive comparison between ‘B12 injection vs tablets,’ exploring the pros and cons to help you make informed choices in your B12 supplementation journey.
Navigating the realm of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Unveiling insights into ‘B12 shot benefits Reddit,’ as we explore user experiences and discussions to shed light on the potential advantages and considerations of B12 supplementation.
Embarking on the exploration of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Emphasizing the crucial principle that ‘healthy habits start early,’ as we delve into the importance of early adoption for optimal well-being and long-term health.
Delving into the realm of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Examining the diverse landscape of ‘vitamin injections,’ exploring the benefits, potential drawbacks, and alternative approaches in the pursuit of overall health and wellness.
Embarking on the exploration of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Unveiling the significance of ‘healthy habits,’ as we navigate through choices and alternatives to promote overall well-being in the realm of B12 supplementation.
Diving into the world of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Unveiling insights while exploring the unique connection to health at ‘Aventura Mall,’ shedding light on options and considerations in B12 supplementation amidst modern lifestyles
Embarking on the exploration of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Emphasizing the importance of professional care with insights from ‘board certified nurses,’ ensuring a comprehensive understanding and safe administration in the realm of B12 supplementation.
Navigating the landscape of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Much like ‘optional cookies,’ we explore the choices available in B12 supplementation, providing insights into the various options and considerations for a personalized approach to health and wellness.
Embarking on the exploration of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Drawing parallels to seamless transactions with ‘payment services,’ we examine the efficiency and choices available in the realm of B12 supplementation, ensuring a smooth and informed health journey.
Exploring B12 Shots & Injections: B12 Shot Purpose Is define for Administration and its Alternatives!
Examining B12 Shots & Injections: Shedding Light on the Definite Reasons Why Would You Need B12 Injections and Exploring Alternatives!
Navigating B12 Shots & Injections: Assessing the Definite Impact of B12 Injection Costs Alongside Exploring Alternatives!
Diving into B12 Shots & Injections: Unveiling the Definite Benefits and Risks of B12 Injections for Humans, Alongside Exploring Alternatives!
Exploring B12 Shots & Injections: Evaluating the Definite Availability and Options for B12 Injections Houston, Alongside Alternatives!
Dissecting B12 Shots & Injections: Investigating the Definite Benefits and Risks of B12 Inkections, Alongside Alternative Options!
Exploring B12 Shots & Injections: Examining the Definite Impact on the Immune System, Alongside Evaluating Alternatives!
Exploring the world of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Uncover the benefits and drawbacks, with a focus on the unique qualities of bedoyecta B12 injections.
Bedoyecta Tri Injections How Often: Dive into B12 Shots & Injections, discover the good and bad, and determine bedoyecta tri injections’ ideal frequency.
Explore the spectrum of B12 Shots & B12 Injections: The Good, Bad, and Alternative! Uncover the benefits of hydroxy B12 injections in this comprehensive guide.
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Exploring the Good, Bad, and Alternative Paths to Enhanced Health, Including Definite Ways to Lose Weight!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Investigating the Pros, Cons, and Alternatives, Along with Definite Insights on Incorporating a Healthy Diet!
B12 Shots & B12 Injections: Delving into the Good, Bad, and Alternative Options, with a Focus on the Role of Lipotropic Injections!








